What is USD/NOK?
USD/NOK refers to the currency pair representing the exchange rate between the US Dollar (USD) and the Norwegian Krone (NOK). In this pair, USD is the base currency and NOK is the quote currency. The exchange rate tells you how many Norwegian Krone are needed to purchase one US Dollar. For example, if the USD/NOK exchange rate is 10.00, it means 1 US Dollar is equivalent to 10 Norwegian Krone. This pair is commonly traded in the forex market and can be influenced by various factors such as economic data, geopolitical events, and changes in interest rates.
USD/NOK Historical Performance

The historical performance of the USD/NOK exchange rate can be analyzed through various time frames and economic contexts. Here’s a general overview of key factors and trends that have influenced the USD/NOK pair:
Economic Factors
- Oil Prices: Norway is a significant oil exporter, so the value of the Norwegian Krone often correlates with global oil prices. When oil prices rise, the NOK typically strengthens against the USD, and when oil prices fall, the NOK can weaken.
- Interest Rates: Interest rate differentials between the US Federal Reserve and Norges Bank (the central bank of Norway) also play a crucial role. Higher interest rates in the US relative to Norway can strengthen the USD against the NOK, and vice versa.
Historical Trends
- Pre-2008 Financial Crisis: Before the 2008 global financial crisis, the USD/NOK exchange rate was relatively stable, with fluctuations primarily driven by changes in oil prices and economic conditions in both countries.
- 2008 Financial Crisis: During the financial crisis, the USD strengthened significantly against many currencies, including the NOK, due to a flight to safety and increased demand for the USD.
- Post-Crisis Recovery: Following the crisis, the NOK strengthened as oil prices recovered, and the exchange rate saw periods of volatility based on fluctuations in oil prices and economic conditions.
Recent Trends (2010s-2024)
- Oil Price Volatility: The NOK has experienced significant volatility in response to oil price fluctuations. For example, the NOK weakened significantly during periods of low oil prices in the mid-2010s.
- COVID-19 Pandemic: The pandemic brought about further volatility in 2020, with a strong USD initially due to its safe-haven status and fluctuations in oil prices impacting the NOK.
- Current Trends: In recent years, the USD/NOK exchange rate has continued to be influenced by global economic conditions, oil prices, and interest rate policies. The rate can also be affected by geopolitical events and changes in global risk sentiment.
What Affects the Price of the USD/NOK Pair
The price of the USD/NOK currency pair is influenced by a range of economic, political, and market factors. Traders and investors watch these variables closely to anticipate changes in the currency pair. For accurate and current analysis, consulting financial news, economic reports, and market analyses is recommended.
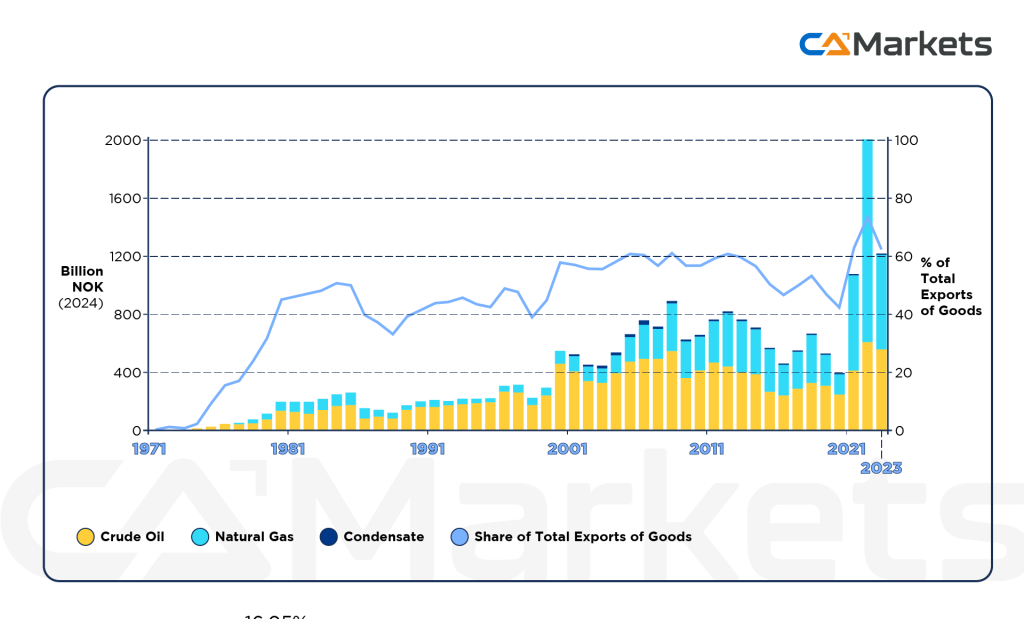
1. Oil Prices:
- Impact: Norway is a significant oil exporter, so changes in global oil prices directly affect the value of the Norwegian Krone (NOK). When oil prices rise, the NOK typically strengthens because higher oil prices boost Norway’s trade balance and economic outlook. Conversely, when oil prices fall, the NOK may weaken.
2. Interest Rates:
- Central Bank Policies: The interest rate decisions of Norges Bank (Norway’s central bank) and the Federal Reserve (US central bank) play a crucial role. Higher interest rates in the US can attract investors seeking higher returns, leading to a stronger USD against the NOK. Conversely, higher rates in Norway can strengthen the NOK.
3. Economic Data:
- GDP Growth: Strong economic growth in either the US or Norway can influence the currency pair. For instance, strong US economic performance can lead to a stronger USD.
- Inflation Rates: Inflation differentials between the US and Norway can impact the exchange rate. Generally, higher inflation in a country devalues its currency relative to others.
4. Political Stability and Economic Policies:
- Government Policies: Fiscal policies, trade policies, and overall economic management in both the US and Norway can influence the USD/NOK exchange rate. Political instability or uncertainty in either country can lead to currency fluctuations.
- Geopolitical Events: Events such as elections, trade negotiations, or geopolitical tensions can impact investor confidence and currency values.
5. Market Sentiment and Speculation:
- Investor Behavior: Market perceptions and speculative actions can affect currency values. For example, if investors expect the USD to strengthen due to anticipated US economic data or policy changes, they might buy USD, driving up the USD/NOK rate.
- Safe-Haven Flows: During periods of global uncertainty or economic stress, the USD is often seen as a safe-haven currency, which can lead to a stronger USD relative to NOK.
6. Trade Balance:
- Exports and Imports: Norway’s trade balance (exports vs. imports) can affect the NOK. A trade surplus (more exports than imports) tends to strengthen the NOK, while a trade deficit can weaken it.
7. Global Economic Conditions:
- Global Growth: Broader global economic conditions impact commodity prices, including oil, and can influence currencies. For example, a global economic slowdown can lead to lower oil prices, impacting the NOK.
8. Central Bank Interventions:
Currency Interventions: Occasionally, central banks may intervene in the foreign exchange market to stabilize or influence their currency’s value. While such interventions are less common in floating exchange rate systems, they can still affect USD/NOK movements.
