What is USD/ZAR?
The USD/ZAR forex pair denotes the exchange rate between the United States dollar (USD) and the South African rand (ZAR). In this pairing, the USD is the base currency, while the ZAR is the quote currency. Therefore, if the USD/ZAR rate is 18.72, it means that 18.72 South African rands are required to buy one US dollar.
The South African rand, introduced in 1961 to replace the South African pound, has a history tied to South Africa’s transition to a republic and departure from the British Commonwealth. Over the years, the rand has undergone various changes and redenominations. Its volatility makes it a notable option for traders interested in speculative opportunities.
USD/ZAR Historical Performance
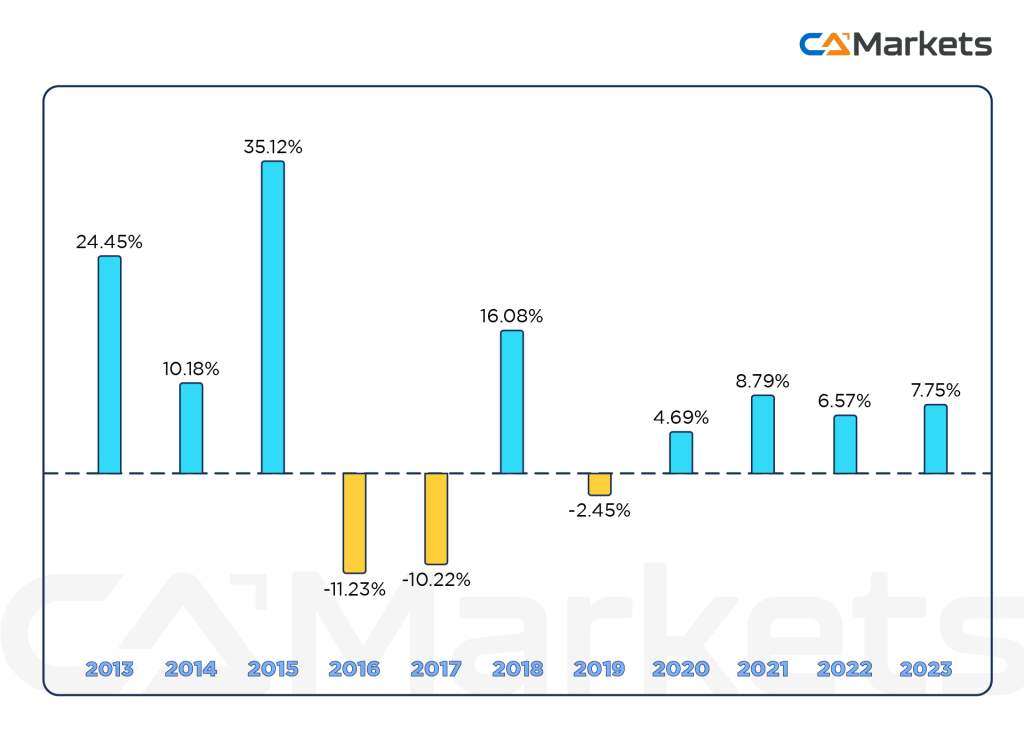
The historical performance of the USD/ZAR forex pair reflects the fluctuating value of the US Dollar (USD) against the South African Rand (ZAR) over time. Here’s an overview of key aspects that influence its historical performance:
Historical Trends
- Long-Term Trends:
- Post-1961: After the South African rand replaced the South African pound in 1961, the exchange rate has seen significant changes. In the early years, the rand was relatively stable but began to experience volatility during periods of economic and political uncertainty.
- Apartheid Era: During the apartheid era (1948-1994), the rand was influenced by international sanctions and economic isolation, leading to periods of depreciation.
- Post-Apartheid and Democratic South Africa:
- 1990s and 2000s: The end of apartheid and South Africa’s transition to democracy led to a more integrated economy. The rand initially strengthened but later faced volatility due to emerging market crises and domestic issues.
- 2008 Financial Crisis: The global financial crisis of 2008 saw significant depreciation of the rand against the USD, reflecting the broader impact on emerging markets.
- Recent Performance:
- 2010s: The rand has faced fluctuations due to commodity price changes, political instability, and economic reforms in South Africa. For instance, the fall in commodity prices, particularly gold and platinum, significantly impacted the rand.
- COVID-19 Pandemic: The COVID-19 pandemic caused sharp volatility in the forex markets, including the USD/ZAR pair, with the rand depreciating against the dollar due to global economic uncertainties and local economic challenges.
Factors Influencing the Movement of USD/ZAR
Understanding the fluctuations in the USD/ZAR exchange rate involves examining several key factors. While central bank policies, geopolitical events, and commodity prices are crucial influencers, they are part of a broader set of elements that shape currency values and exchange rates. Here’s a detailed look at these factors:
Central Bank Policies
- Interest Rates: Central banks adjust interest rates to manage economic growth and inflation. Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, which can strengthen a currency by increasing demand. Conversely, lower interest rates might weaken a currency due to reduced investment inflows.
- Inflation: Central banks target inflation rates through their monetary policies. Low inflation generally supports a stronger currency, as it preserves purchasing power. High inflation, on the other hand, can erode currency value.
- Currency Interventions: Central banks might also engage in direct currency market interventions or implement policies that affect exchange rates. These interventions can influence the USD/ZAR rate by affecting supply and demand dynamics.
Geopolitical Events
- Political Stability: Political events and stability in South Africa and the US can significantly impact the USD/ZAR rate. Political uncertainty or instability, such as corruption scandals or policy shifts, can undermine investor confidence and affect currency values.
- Economic Performance: Economic performance indicators, including GDP growth, employment rates, and trade balances, also play a role. Strong economic performance generally supports currency strength, while economic troubles can lead to depreciation.
- Historical Context: For example, during South Africa’s apartheid era, international sanctions and political isolation led to a significant depreciation of the rand. Such geopolitical factors continue to play a role in shaping the currency’s value.
Commodity Prices
- Export Reliance: South Africa is heavily reliant on commodity exports, earning the rand the label of a ‘commodity currency’. Key exports include gold, platinum, and iron ore. Fluctuations in commodity prices can directly impact South Africa’s export revenues and, consequently, the rand’s value.
- Gold and Precious Metals: In 2021, gold was South Africa’s primary export, constituting 14% of total exports with a value of $20.1 billion. Precious stones, metals, and coins were the largest export category as of 2022, valued at around $25 billion. Changes in global commodity prices can thus affect South Africa’s trade balance and influence the USD/ZAR exchange rate.
Additional Factors
- Global Economic Conditions: Global economic trends, such as economic growth rates in major economies and international trade dynamics, can impact currency pairs. For instance, global economic slowdowns or booms can affect demand for commodities and influence the USD/ZAR rate.
- Market Sentiment: Investor sentiment and risk appetite can drive fluctuations in currency values. In times of global uncertainty or financial stress, investors may seek safe-haven currencies like the USD, impacting the USD/ZAR exchange rate.
- Trade Policies: Changes in trade policies or agreements between the US and South Africa, or with other key trading partners, can also affect the exchange rate by altering trade flows and economic interactions.
These factors interplay to influence the USD/ZAR exchange rate, making it essential for traders and investors to consider a broad range of economic, political, and market conditions when analyzing currency movements.
