Definition of a Limit Order
In Forex CFD trading, a limit order is a directive given to a broker to execute a trade at a predetermined price or better. Rather than entering the market immediately at the current price, traders use limit orders to specify the exact price they wish to buy or sell a currency pair.
For instance, if the current EUR/USD rate is 1.2000 and a trader expects a decline, they might set a buy limit order at 1.1950. This order will only be executed if the market price drops to 1.1950 or lower, ensuring the trade is made at the desired price level. Limit orders offer traders control over their entry and exit points, allowing them to manage risk and potentially improve profitability by capturing favorable price movements without constant market monitoring. However, there’s a risk of the order not being filled if the market doesn’t reach the specified price, requiring traders to monitor their orders accordingly.
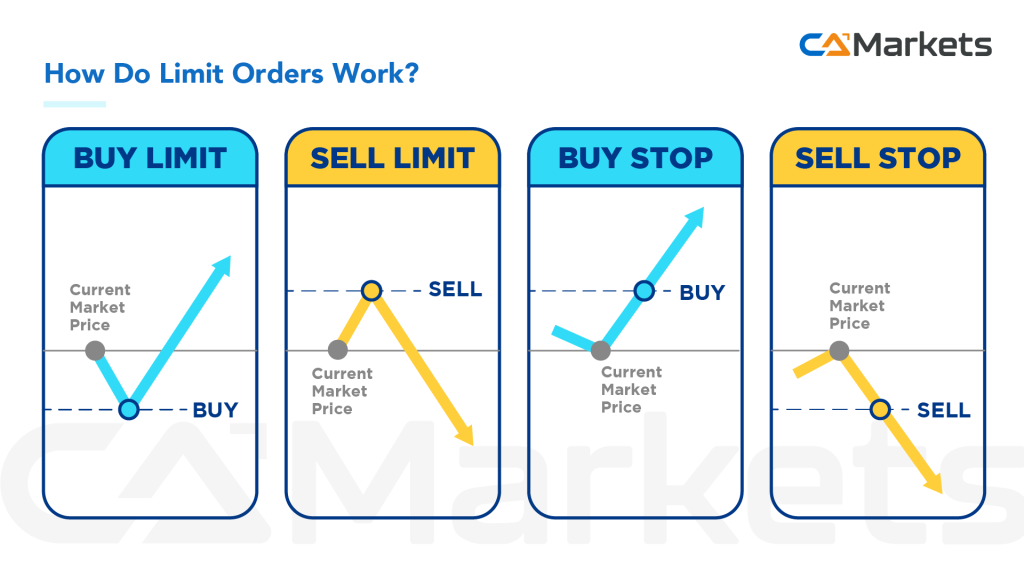
How do limit orders work in your trade?
Buy Limit Orders: a buy limit order is a specific type of order where a trader instructs their broker to BUY a currency pair at a price lower than the current market price.
Sell Limit Orders: a sell limit order is a specific instruction given by a trader to their broker to SELL a currency pair at a price higher than the current market price.
Buy Stop Orders: a buy stop order is a type of order where a trader instructs their broker to BUY a currency pair at a price higher than the current market price.
Sell Stop Orders: a sell stop order is a type of order where a trader instructs their broker to SELL a currency pair at a price lower than the current market price.
Definition of Stop Limit Orders
Stop limit orders combine features of stop orders and limit orders into a single order type, allowing traders to specify both a trigger price and a limit price for execution.
Trigger Price (Stop Price): This is the price at which the stop limit order is activated and becomes a limit order. For example, in a sell stop limit order, if the market price drops to or below the stop price, the order is triggered.
Limit Price: Once triggered, the limit price specifies the minimum price at which the trader is willing to sell (in the case of a sell stop limit order) or buy (in the case of a buy stop limit order). This means that after the stop price is reached, the order will only be executed at the limit price or better.
Example Scenarios:
- Sell Stop Limit Order: Suppose the current market price of EUR/USD is 1.2000, and a trader expects a decline but wants to limit the price at which they sell. They might place a sell stop limit order with a stop price of 1.1950 and a limit price of 1.1930. If the market price drops to 1.1950 or below, the order is triggered. It then becomes a limit order to sell at 1.1930 or better. If the market falls quickly and reaches 1.1950 but then rebounds above 1.1930 without reaching 1.1930, the order may not be filled.
- Buy Stop Limit Order: Conversely, if a trader believes the price will rise after reaching a certain level, they might place a buy stop limit order. For instance, with EUR/USD at 1.2000, they could set a buy stop at 1.2050 and a limit price at 1.2070. If the market price reaches 1.2050 or higher, the order is triggered and becomes a limit order to buy at 1.2070 or better.
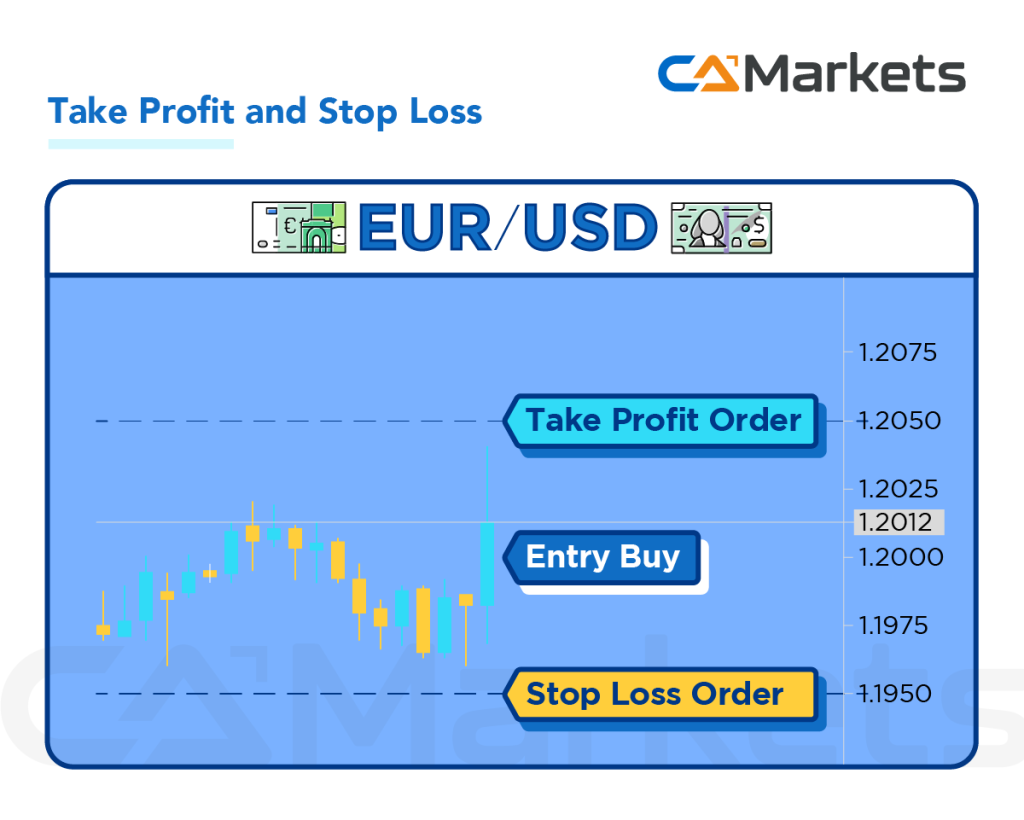
Definition of Take Profit
Take Profit (TP) order is a predefined instruction given by a trader to their broker to automatically close a position when a certain profit level has been reached. It is a type of limit order that is used to lock in profits once the market price moves favorably in the trader’s direction.
How does Take Profit work?
Setting the Price: When entering a trade, a trader can specify a Take Profit price, which is the target price at which they want their position to be automatically closed to secure the profit. For example, if a trader buys EUR/USD at 1.2000 and expects the price to rise, they might set a Take Profit order at 1.2050.
Execution Condition: Once the market price reaches the specified Take Profit level of 1.2050, the broker executes the order and closes the position at the best available price. This ensures that the trader locks in the profit generated from the trade.
Purpose and Strategy: Take Profit orders are used to manage trades more efficiently by automatically closing them at predetermined profit targets. This allows traders to avoid the pitfalls of emotional trading decisions and ensures that profitable trades are capitalized upon effectively.
Definition of Stop Loss
a stop loss order is a risk management tool used by traders to limit potential losses on a trade. It is an instruction given to a broker to automatically close a position when the market price reaches a specified level, known as the stop price.
How does stop loss work?
Setting the Stop Price: When entering a trade, a trader can set a stop loss order at a price level that represents the maximum amount of loss they are willing to tolerate. For example, if a trader buys EUR/USD at 1.2000, they might set a stop loss order at 1.1950. This means that if the market price drops to 1.1950 or below, the stop loss order will be triggered.
Execution Condition: Once the market price reaches or falls below the specified stop price (1.1950 in the example), the stop loss order becomes a market order and is executed at the best available price. This automatic execution helps ensure that the trader exits the trade and limits further potential losses beyond the predetermined threshold.
Purpose and Strategy: Stop loss orders are crucial in managing risk by helping traders control the downside risk of their trades. They provide a level of protection against adverse market movements that could lead to significant losses if the trade moves against the trader’s expectations.