The DAX 40 is a stock market index that represents the performance of the 40 largest and most liquid companies listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange in Germany. It was introduced in September 2021, expanding from its previous iteration, the DAX 30, which only included 30 companies.
The DAX 40 includes major players from various sectors, such as automotive, finance, and technology, reflecting the broader German economy. The index is often used as a benchmark for the performance of the German stock market and is a key indicator for investors and analysts tracking economic trends in Germany.
How is the DAX 40 calculated?
To be included in the DAX, companies must meet several fundamental requirements. They need to be listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange, maintain a minimum free float of 10%, have a legal or operational headquarters in Germany, and publish their quarterly and annual reports on time.
The selection of companies for the index is determined by their free-float market capitalization and is reviewed quarterly. Additionally, no single company can have a weighting of more than 10% in the index.
Dax companies – Sector Breakdown
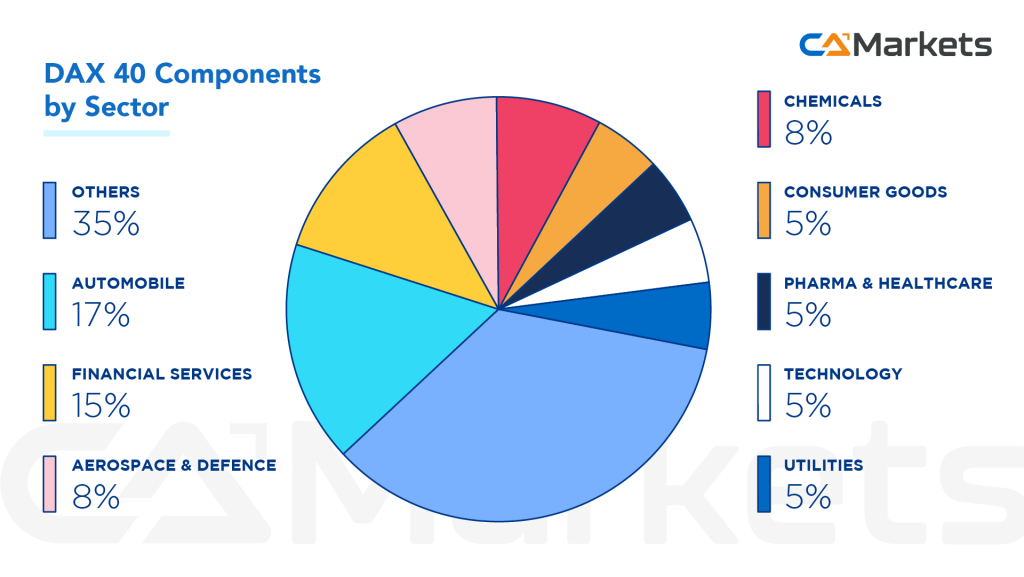
As illustrated in the chart above, the Automobile sector is the largest, representing nearly 17% of the index and including major players like Volkswagen and Daimler. It is closely followed by the Financial Services sector, which accounts for 15%. The Aerospace & Defence and Chemicals sectors are next, while the Pharma & Healthcare sector together comprises approximately 5% of the index.
How to trade DAX 40?
Contract for Difference (CFDs) offer a cost-effective and efficient way to trade the DAX. Typically, brokers provide two types of CFDs: one based on the cash index (GER30) and another based on the underlying futures contract (DAX30.fs).
With CFDs, you can speculate on the direction of the DAX without owning the actual index or its constituents. This method allows for leverage and the flexibility to go both long and short, which can be particularly advantageous during market downturns. Instead of rebalancing your entire portfolio—which can be costly and challenging to time effectively—you can use CFDs to profit from falling prices.
Your choice between the cash CFD (GER30) and the futures CFD (DAX30.fs) will depend on your trading style. The GER30, with its low spreads, is generally better suited for short-term trades. In contrast, the DAX30.fs may be preferable for long-term trading, as it does not incur swap charges.
The average return on the Dax 40
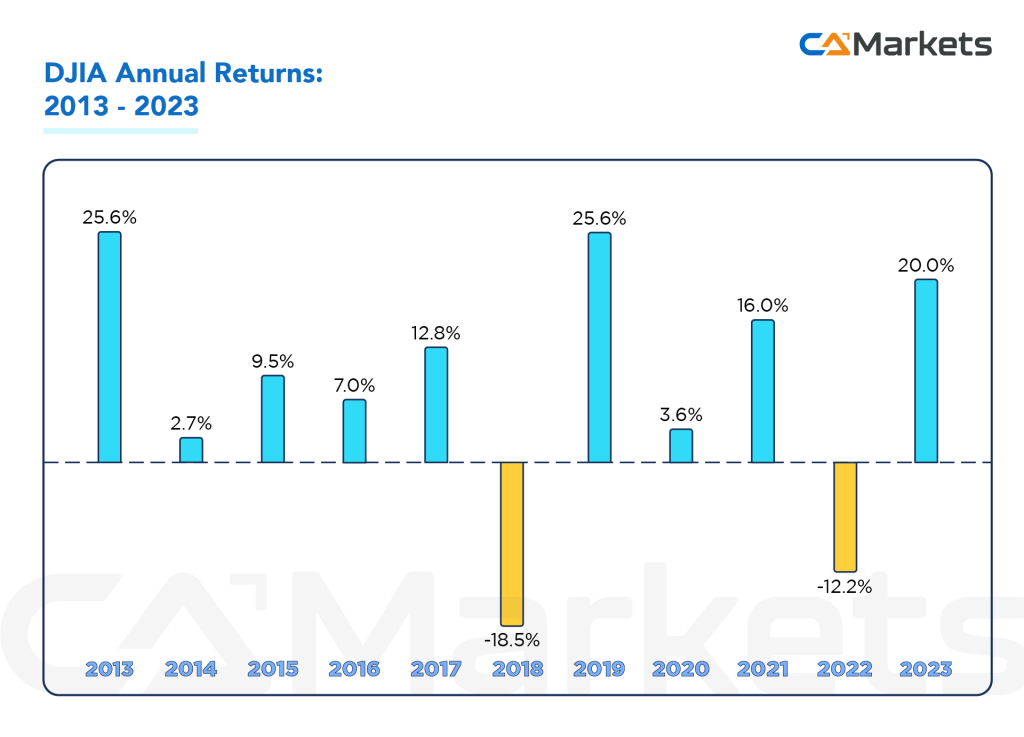
Over the last 10 years, the average annual return of the DAX 40 has varied significantly due to market conditions, economic cycles, and global events. Historically, the DAX 30 (now DAX 40) has had an average annual return of approximately 7-10%, though this range can fluctuate based on the specific time period and market performance.
For the most current and precise data, including the average return over the last decade, you would typically consult financial databases, index providers, or historical performance reports from financial institutions. These sources provide updated figures and detailed breakdowns of returns over various time frames.
