Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading or currency trading, involves the buying and selling of currencies on the foreign exchange market with the aim of making a profit. It is one of the largest and most liquid financial markets globally, where currencies from various countries are traded against each other.
Understanding Exchange Rates
An exchange rate is the rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another. It represents the value of one currency relative to another currency. Exchange rates can be quoted in different ways:
- Direct Exchange Rate: This is the price of one unit of a foreign currency in terms of the domestic currency. For example, if the exchange rate for USD/EUR is 0.85, it means 1 US Dollar can be exchanged for 0.85 Euros.
- Indirect Exchange Rate: This is the reciprocal of the direct exchange rate, showing the price of one unit of domestic currency in terms of a foreign currency. Using the example above, the indirect rate for EUR/USD would be approximately 1.18, meaning 1 Euro can be exchanged for 1.18 US Dollars.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
Exchange rates are determined by various factors and can fluctuate due to changes in supply and demand dynamics in the foreign exchange market.
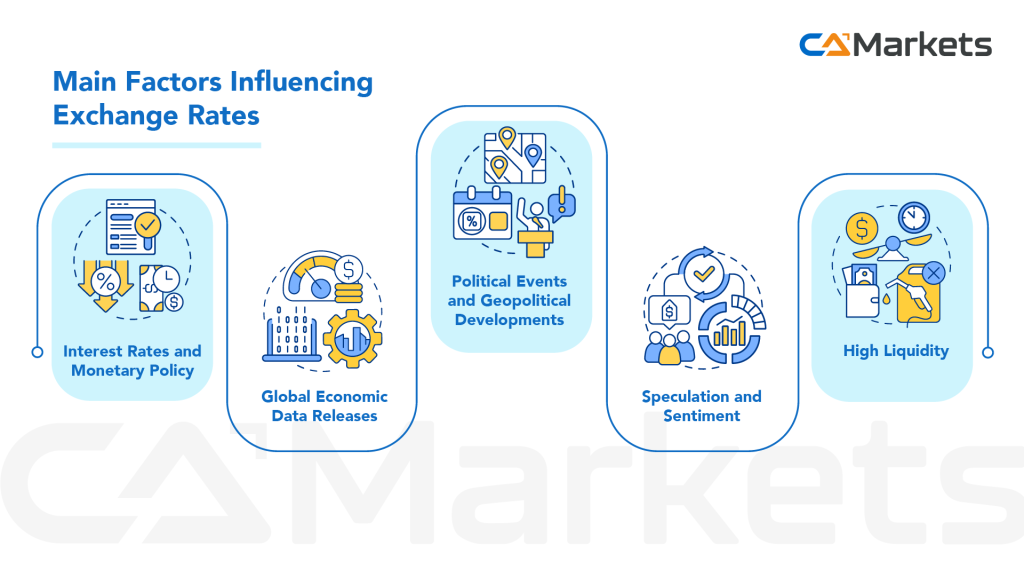
The key factors include:
- Interest Rates and Monetary Policy: Changes in interest rates and monetary policy decisions by central banks influence exchange rates by affecting investor expectations for future economic conditions and capital flows. Higher interest rates typically attract foreign investment, strengthening a currency, while lower rates may lead to depreciation.
- Global Economic Data Releases: Economic indicators such as GDP figures, employment reports, inflation data, and central bank announcements can have a significant impact on exchange rates. These releases often lead to immediate market reactions as traders adjust their positions based on new information.
- Political Events and Geopolitical Developments: Political stability, elections, policy decisions, and geopolitical tensions can affect investor confidence and currency valuations. Uncertainty or unexpected events can lead to rapid movements in exchange rates as market participants reassess risks.
- Speculation and Sentiment: Market sentiment and speculative trading play a significant role in short-term exchange rate movements. Traders and investors may buy or sell currencies based on their expectations of future price movements, amplifying volatility in the market.
- High Liquidity: The forex market is the most liquid financial market globally, meaning there is a high volume of trading activity and a large number of participants buying and selling currencies at any given time. This liquidity ensures that transactions can be executed quickly and at current market prices
